TMP36 LCD Temperature Display
Written by Luka Kerr on April 1, 2018
The TMP36 sensor is a temperature sensor, and using it with a 16 pin LCD display is a nice way to display the current temperature.
The first thing you must do it include the LCD library so that text can be displayed. This is shown below
// include the library code:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
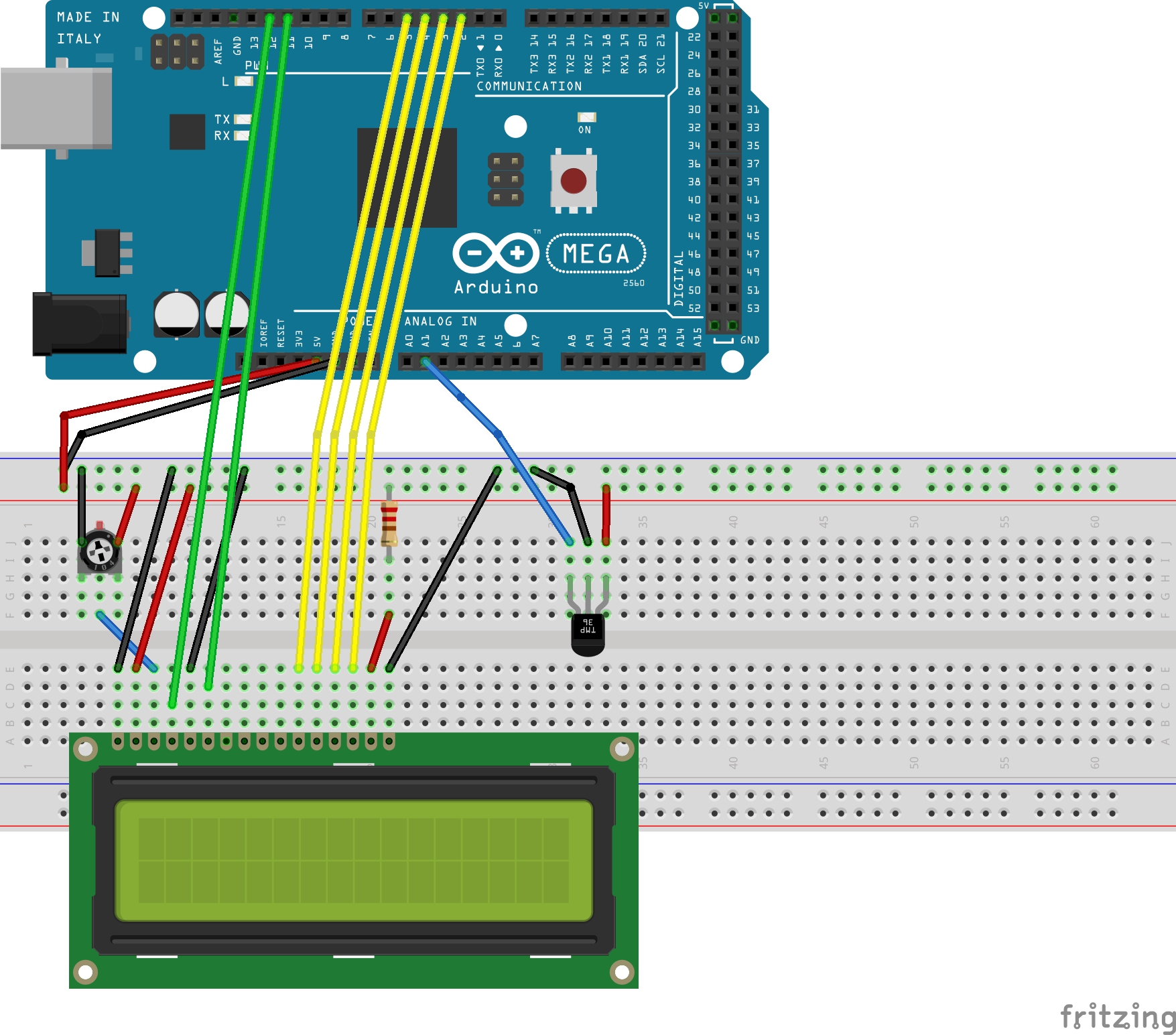
Next you need to specify which pins you want to use to display the output. For this example we are using pins 12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2. You can see more clearly in the Fritzing diagram at the bottom where these pins are located.
// Initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
Next we declare the analog input pin for the TMP36, for this example we are using pin 1.
int tempPin = 1;
Next is the setup function. This returns nothing but sets up the properties of the LCD display including its width in characters, height in characters and the text that is displayed.
void setup() {
// Setup the LCD number of columns and rows
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.print("Temp ");
lcd.print((char)223);
lcd.print("C = ");
}
Finally we use the loop function which continuously loops through the TMP36’s input and performs a calculation to convert the analog reading into temperature (degrees Celsius). This then gets displayed on the LCD screen, and updates every 1000ms, or every 1 second.
void loop() {
float voltage, temp;
int reading = analogRead(tempPin);
temp = 1.8 * ((reading + 30) / 8.3) + 32;
temp = ((temp - 32) * 5) / 9;
// Print result to lcd display
lcd.setCursor(10, 0);
lcd.print(temp);
// Sleep
delay(1000);
}
In the end this is what your code should look similar to.
You will need to modify the
tempvariable’s calculation if you want it in fahrenheit.
// include the library code:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
// Initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
int tempPin = 1;
void setup() {
// set up the LCD's number of columns and rows:
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.print("Temp ");
lcd.print((char)223);
lcd.print("C = ");
}
void loop() {
float voltage, temp;
int reading = analogRead(tempPin);
temp = 1.8 * ((reading + 30) / 8.3) + 32;
temp = ((temp - 32) * 5) / 9;
// print result to lcd display
lcd.setCursor(10, 0);
lcd.print(temp);
// sleep...
delay(1000);
}
Fritzing Diagram
The wiring for the display and temperature is shown below: